
|
|
 |
Cold,
snowy, windy. When you hear those words they make you think
of mountains. The Alpine biome is like winter is to people
in New England; snow, high winds, ice, all the typical
winter things. In Latin the word for 'high mountain' is
'alpes'. That is where today's word alpine comes
from. Alpine
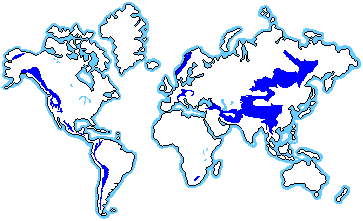
biomes are found in the mountain regions all around the
world. They are usually at an altitude of about 10,000 feet
or more. The Alpine biome lies just below the snow line of a
mountain. As you go up a mountain, you will travel through
many biomes. In the North American Rocky Mountains you begin
in a desert biome. As you climb you go through a deciduous
forest biome, grassland biome, steppe biome, and taiga biome
before you reach the cold Alpine biome. In the
summer average temperatures range from 10 to 15° C . In
the winter the temperatures are below freezing. The winter
season can last from October to May. The summer season may
last from June to September. The temperatures in the Alpine
biome can also change from warm to freezing in one
day. Because
the severe climate of the Alpine biome, plants and animals
have developed adaptations to those conditions. There are
only about 200 species of Alpine plants. At high altitudes
there is very little CO2, which plants need to carry on
photosynthesis. Because of the cold and wind, most plants
are small perennial groundcover plants which grow and
reproduce slowly. They protect themselves from the cold and
wind by hugging the ground. Taller plants or trees would
soon get blown over and freeze. When plants die they don't
decompose very quickly because of the cold. This makes for
poor soil conditions. Most Alpine plants can grow in sandy
and rocky soil. Plants have also adapted to the dry
conditions of the Alpine biome. Plant books and catalogs
warn you about over watering Alpine plants. Alpine
animals have to deal with two types of problems: the cold
and too much high UV wavelengths. This is because there is
less atmosphere to filter UV rays from the sun. There are
only warm blooded animals in the Alpine biome, although
there are insects. Alpine animals adapt to the cold by
hibernating, migrating to lower, warmer areas, or insulating
their bodies with layers of fat. Animals will also tend to
have shorter legs, tails, and ears, in order to reduce heat
loss. Alpine animals also have larger lungs, more blood
cells and hemoglobin because of the increase of pressure and
lack of oxygen at higher altitudes. This is also true for
people who have lived on mountains for a long time, like the
Indians of the Andes Mountains in South America and the
Sherpas of the Himalayas in Asia.
bibliography: "Himalayas",
http://encarta.msn.com/find/,
(June 2000). "General
Ecology, EEOB 404", http://www.tulane.edu/~eeob/Courses/Ecology_Materials/arctic_alpine_99f.html,
(June 2000).
|
|
|
|
|
